
The General Theory of
Relativity is the geometric theory of gravitation published by Albert
Einstein in 1915. General relativity generalizes special relativity
and refines Newton's Laws of Gravitation, providing a unified
description of gravity as a geometric property of space and time or
space-time. In particular, the curvature of space-time is directly
related to the energy and momentum of whatever matter and radiation
are present.

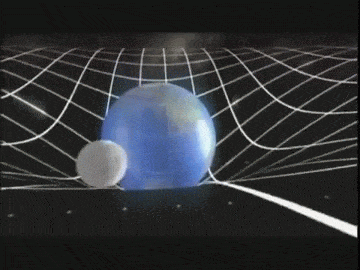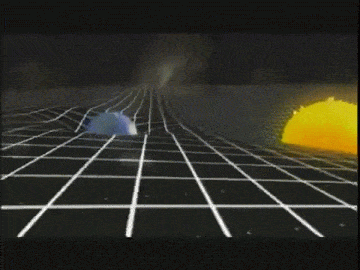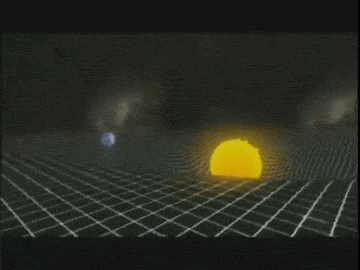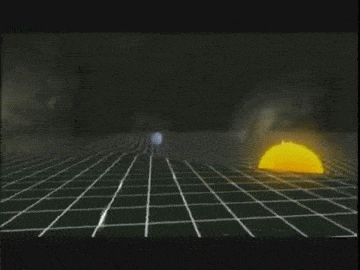
The central idea of
general relativity is that space and time are two aspects of
space-time. The space-time is curved when there is gravity, matter,
energy and momentum. The general relativity used the notion of curved
space-time to describe the effects of gravity and accelerated motion.
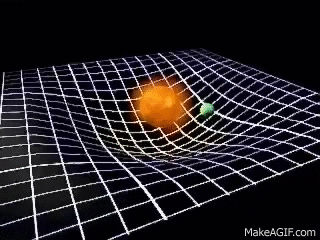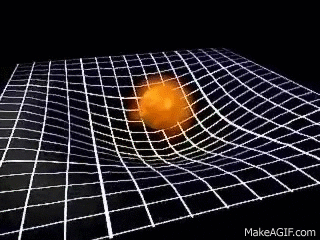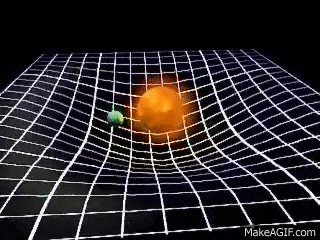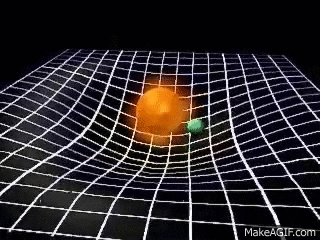
For example, the Sun and
the Earth can be seen in the valley of the space-time. Due to the
gravitational force, the Sun pulls the Earth towards it. But the
Earth does not roll towards the Sun because it is moving very fast and
the centrifugal force exists, the Earth moves sideways. This sideways
motion of Earth makes the distance between the Earth and the Sun
increases. The force pulling the Earth towards the Sun is the same as
the centrifugal force of the Earth. The Earth is being pulled towards
the Sun and also moving away at the same time and hence it stays at
about the same distance. This how the Moon orbits the Earth.
Like this, the general
relativity has predicted the reasons for the following incidences
happening in the Universe such as;
>> As light gets
closer to the Sun, it bends towards the Sun twice as much as
classical physics predicts.
 |
| Bending of light near the Sun |
>> The perihelion of the planet Mercury rotates along its orbit more than is expected under Newtonian physics.
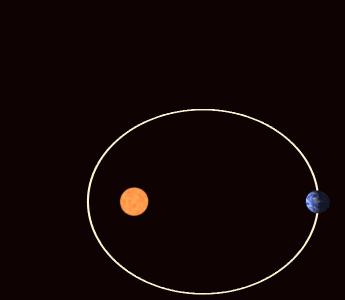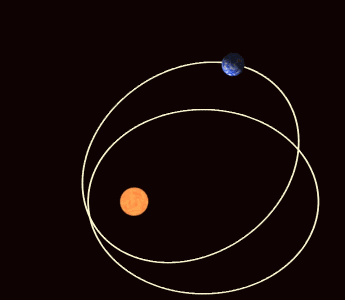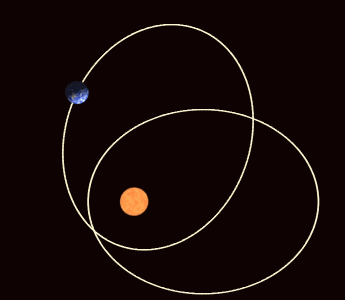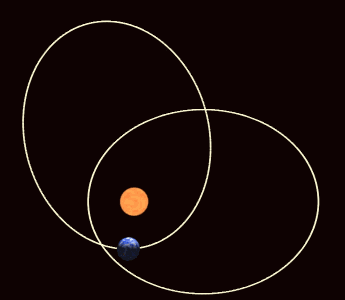 |
| Precession of the Perihelion of Mercury |
>> The Redshift from gravity, that is, when light moves away from an object with gravity (moving away from the center of the valley), it is stretched into longer wavelengths.
 |
| Redshift of Light from Gravity |
Comments
Post a Comment